Introduction: Make Your Text Clear, Accessible & SEO-Ready
Struggling to make your website’s text both readable and search-engine friendly? HTML5 text content semantic tags are your secret weapon. These tags add meaning, clarity, and structure to your content, making it more accessible for all users while boosting SEO.
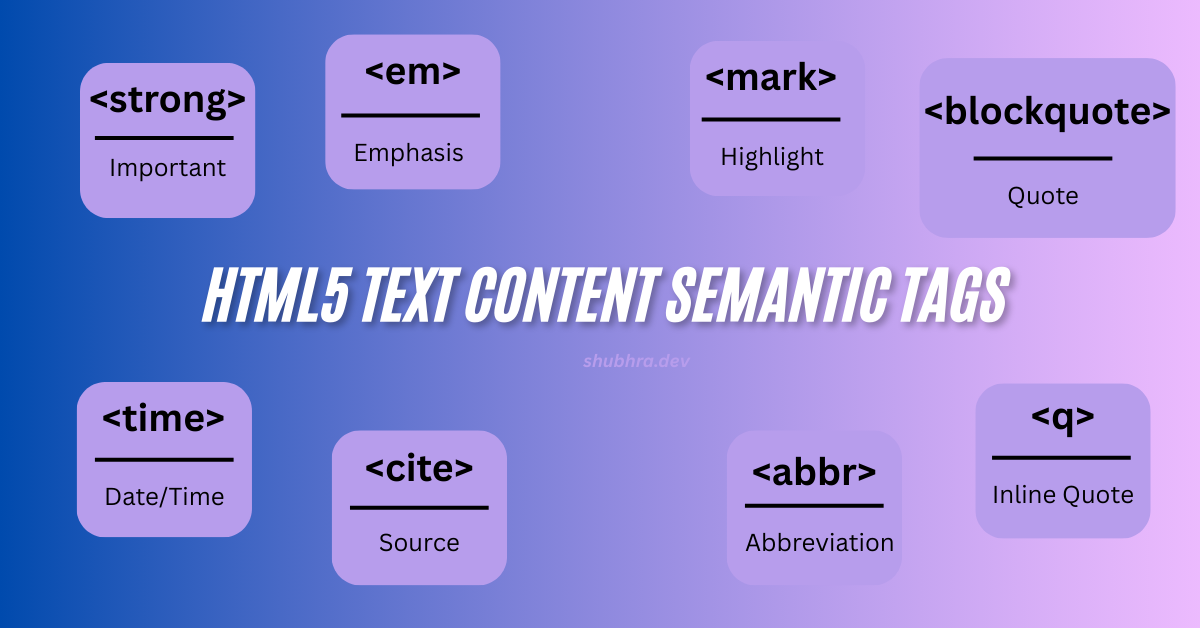
In this guide, you’ll learn how to use tags like <strong>, <mark>, <blockquote>, <time>,
- Highlight key content for users and search engines.
- Make your content inclusive and screen-reader friendly.
- Avoid common mistakes that reduce your SEO potential.
By the end, you’ll be ready to create text content that’s both human-friendly and SEO-optimized.
Why HTML5 Text Content Semantic Tags Are Essential
Semantic text tags don’t just style your text- they give it purpose and meaning. Unlike <b> or <i>, semantic tags tell browsers, search engines, and assistive tools what your text represents, not just how it looks.
Here’s why using these tags matters:
- 🔑 Boost Keyword Relevance: <strong> and <mark> signal important content to search engines.
- 📢 Improve Accessibility: Screen readers understand semantic tags better than plain bold or italic.
- 📈 Increase Engagement: Clear, meaningful text keeps users reading longer and improves trust.
For a deeper dive into combining these with page layout, check out our Master HTML5 Page Structure Semantic Tags for Smarter Layouts and also check out our HTML5 Semantic Tags Overview for a strong foundation.
Master Key HTML5 Text Content Semantic Tags
Let’s break down the most important semantic text tags and how to use them:
| Tag | Purpose | Example Use |
| <strong> | Indicates text of strong importance | <strong>Do not share your password</strong> |
| <em> | Emphasized text, usually italic | I <em>really</em> love coding! |
| <mark> | Highlights important content | New features include <mark> 24/7 support </mark> |
| <blockquote> | Longer quoted sections | <blockquote cite=”https://example.com”>Quote text here</blockquote> |
| <q> | Short, inline quotations | She said, <q>HTML5 is amazing!</q> |
| <time> | Dates, times, durations (machine-readable) | <time datetime=”2025-09-06″>September 6, 2025</time> |
| <cite> | Titles of works or sources | <cite>John Doe</cite> |
| <abbr> | Abbreviations with full form | <abbr title=”HyperText Markup Language”>HTML</abbr> |
These tags help your content communicate meaning, making it readable for humans and understandable for search engines.
How to Use Semantic Text Tags Effectively
To get the most out of semantic tags:
- Choose the Right Tag
- <strong> for crucial info.
- <em> for subtle emphasis.
- <mark> for highlighting keywords or new content.
- <blockquote> for long quotes, <q>
for inline quotes.
- Enhance Accessibility
- Always add title to <abbr>:
<abbr title="HyperText Markup Language">HTML</abbr
- Use datetime for <time>:
<time datetime="2025-09-06">September 6, 2025</time>
- Always add title to <abbr>:
- Combine with Structural Elements
- Pair with <article>, <section>, or <aside> for cohesive pages.
- Example: <article><h2>Title</h2><p>Text with <strong>importance</strong></p></article>
- Style Without Losing Meaning
- Use CSS to style semantic tags but don’t rely on styling alone for meaning:
mark { background-color: #ffeb3b; }
- Use CSS to style semantic tags but don’t rely on styling alone for meaning:
SEO & Accessibility Benefits
Semantic text tags improve your site for both users and search engines.
SEO Benefits
- Keyword Highlighting: <strong> and <mark> signal important content.
- Rich Snippets: <time> helps search engines understand dates for events or posts.
- Credibility Signals: <blockquote> and <cite> provide context for quoted content.
Accessibility Benefits
- Screen Reader Support: Tags convey meaning, not just style.
- Better Navigation: <abbr> and <time> improve comprehension for assistive tools.
- Inclusive Design: Ensures your site is usable for people with visual or cognitive impairments.
Practical Examples of Semantic Text Tags
Example 1: Blog Post Snippet
<article>
<h2>Why Semantic HTML Matters</h2>
<p>Published on <time datetime="2025-09-06">September 6, 2025</time></p>
<p>Semantic HTML is <strong>crucial</strong> for modern web development. As <cite>John Doe</cite> once said, <q>Good markup is the foundation of a great website.</q></p>
<blockquote cite="https://example.com/source">
<p>Using semantic tags like <mark>strong</mark> and <em>em</em> improves both accessibility and SEO.</p>
</blockquote>
<p>Learn more in our <a href="https://example.com/html5-page-structure">HTML5 Page Structure Guide</a>.</p>
</article>
Example 2: Product Description
<section>
<h2>Product Overview</h2>
<p>Our <strong>UltraFast Hosting</strong> plan, launched on <time datetime="2025-01-01">January 1, 2025</time>, offers unmatched speed.</p>
<p>Key features include <mark>24/7 support</mark> and <abbr title="Secure Sockets Layer">SSL</abbr> encryption.</p>
<p><q>Best hosting I’ve ever used!</q> — <cite>Tech Magazine</cite></p>
</section>
Avoid These Common Semantic Tag Mistakes
- Using <b> or <i> instead of <strong> or <em>.
- Overusing <mark> – only highlight essential content.
- Forgetting attributes like title for <abbr> or cite for <blockquote>.
- Incorrect <time> format (YYYY-MM-DD is correct).
- Relying on style alone – semantic meaning is more important than bold or color.
Conclusion: Transform Your Text Content Today
By mastering HTML5 text content semantic tags, you’ll make your content:
- Clear and readable for visitors
- SEO-optimized for search engines
- Accessible for all users
Start using these tags in your projects today, pair them with structural and media elements, and watch your site’s clarity, engagement, and search rankings soar.
To deepen your understanding of HTML5 text content semantic tags and enhance your web development skills, explore these trusted resources. For official specifications, visit the W3C HTML5 Specification. For practical accessibility guidelines, refer to the W3C Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI).
